Situated strategically at the crossroads of Africa, Asia, and Europe, Djibouti has emerged as a vital gateway connecting these three continents. This small but significant country, located in the Horn of Africa, offers a unique combination of geographical advantages, economic opportunities, and political stability. With its strategic location, world-class infrastructure, and diverse cultural heritage, Djibouti has become a crucial hub for international trade, commerce, and logistics.
Geographical Significance
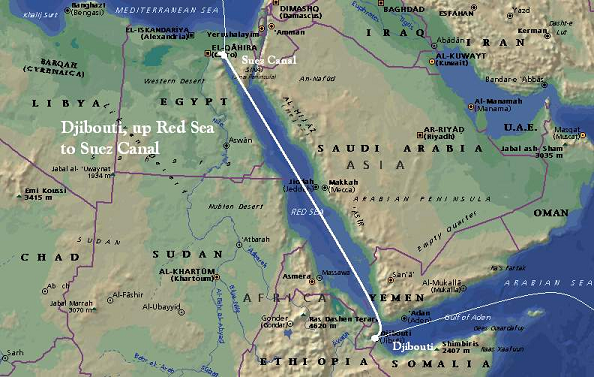
Djibouti’s geographic location makes it an ideal gateway between Africa, Asia, and Europe. It lies on the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, which connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden, and serves as a gateway to the Suez Canal, one of the world’s busiest shipping routes. This proximity to major maritime trade routes has enabled Djibouti to establish itself as a key transshipment and logistics hub.
The country’s coastline stretches for approximately 370 kilometers, providing access to the Indian Ocean. This coastline hosts the Port of Djibouti, one of the largest and most efficient ports in the region. The port handles a significant volume of cargo destined for African, Asian, and European markets, facilitating trade and investment across these continents.
This openness to the sea and its strategic location are precisely what has made Djibouti a popular destination for global powers wishing to access markets or protect the many trade routes that crisscross the region. Today, Europeans, Americans and Asians are jostling for a spot under the Djiboutian sun.



Economic Opportunities
Djibouti has attracted significant foreign investment, leading to rapid economic growth and development. The country has invested heavily in developing world-class infrastructure, including ports, railways, airports, and free trade zones. These investments have positioned Djibouti as a major logistics and transshipment hub, offering a wide range of economic opportunities.
The Port of Djibouti, operated by the Djibouti Ports and Free Zones Authority, plays a vital role in facilitating trade between Africa, Asia, and Europe. It serves as a major gateway for imports and exports, handling goods destined for landlocked countries in East Africa, such as Ethiopia, South Sudan, and Uganda. The port’s efficiency, connectivity, and modern facilities have attracted numerous international companies, making Djibouti a crucial link in global supply chains.
In addition to its maritime infrastructure, Djibouti has invested in a modern railway network. The recently completed Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway connects Djibouti’s port with the Ethiopian capital, providing a reliable and efficient transportation link between the landlocked country and the sea. This railway has significantly reduced transportation costs and transit times, further enhancing Djibouti’s appeal as a gateway to Africa, Asia, and Europe.



Political Stability and Regional Cooperation
Djibouti’s political stability and commitment to regional cooperation have played a crucial role in establishing its position as a gateway to three continents. The country has maintained a relatively peaceful environment amidst regional conflicts and has actively pursued diplomatic engagement with neighboring countries.
Djibouti is a member of the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD), a regional organization that promotes economic cooperation and integration in East Africa. Through IGAD, Djibouti has fostered partnerships with neighboring countries, fostering regional trade and connectivity.
Furthermore, Djibouti has established diplomatic ties with a wide range of countries, including those in Africa, Asia, and Europe. This has resulted in increased foreign direct investment, trade agreements, and technical cooperation.
